Electronic Components
Resistors
Background Information
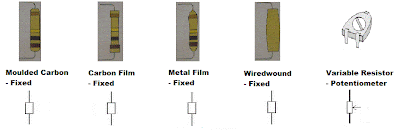
Resistors come in many shapes and sizes and used to divide or limit current while in electrical system but most importantly used to protect electrical and electronic components from being damaged while in it's circuit. But in the Automotive industry there is two types of resistors that are mainly used, these two types of resistor are named fixed and variable resistors, the fixed resistor are made in different shapes the practical terms for these resistor are known as; moulded carbon, carbon film, metal film and wirewound. For the variable resistor it comes in different shapes but are classed as the same component the practical term for this resistor is known as a potentiometer.
As I said resistors come in many sizes this doesn't just mean the it's actual size it also means the resistance it produces while in the circuit, this can range for 1 Ohm (Ω symbol of unit of measurement) Ohm to up to 9.1M Ohms. The way this is calculated is by the coloured bands that are on the resistor plus the tolerance must be calculated (the range of resistors that the resistor can handle). The measurement of resistance is calculated in Ohms, Ohms were discovered in the last half of the 19th century by a German man named Georg Simon Ohm. Although several empirically derived standard units for expressing
electrical resistance were developed in connection with early telegraphy
practice.Variable Resistors are more commonly known as potentiometer. the way it is used is to adjust the vale of the resistor depending on you are controlling in the circuit e.g. an LED can be use by potentiometer to brighten and dim the LED, the way to adjust the potentiometer is to turn the knob with a screwdriver that is on the potentiometer and the resistance will change depending on how high or low you put the potentiometer.
As the resistors are wired up to the power source it will can the value of power as it is run through it There is three ways that the resistor and variable resistor can be wired up and they are known as series, parallel and compound circuits (series and parallel together).
Using any of these three will change the voltage in the different circuit and will can the resistance will increase depending on the resistors that are used. The way that this is calculated is I = V / R or V = I x R or (Rn / Rt) x Vs, but if you trying to find the then the calculations for this will be R = V / I (for the one resistor), or I = Vd / R1= A then Vd / A = R2.
Technical Explanation
A resistor is a basic component of an electrical circuit that resist or limits the flow of current running through it. A resistor has two terminal that are non polarity-conscious, where electric current passes through intently dropping the voltage of the current through one terminal to the other. A resistor is used to maintain a known safe current through an electrical or electronic component.Symbols
The symbol on the left is used around the world for symbolizing the resistor while in America they use the symbol on the right to for symbolizing the resistor.Testing Procedures
Problems
If a resistor was connected in a series circuit and was to shorts out it should be right to assume that the resistor will break the circuit, but the fact is that the if the resistor is damage due to the excessive voltage the resistor will short out but not be destroyed, this mean that circuit will still pass through it but the resistance that the resistor is mean't to resist it will only resist a small amount circuit. But if a resistor is to fully blow this means that the circuit will no longer be connected thus the circuit broken and will no longer work.Reflection
While using resistors in all of my circuits that I wired up, I had to calculate some resistors, use a multimeter to find voltage drop and available voltage and use resistors to be able to prevent damage to other components. Using resistors is a cheap component that can be replaced when it is shorted or blown. So it is an effective component to protect other components by cutting the current running through the circuit or place in a circuit to be able to restrain the amount of current going through the circuit and dropping the voltage so the other components can not be damaged by excess voltage.Diodes
Background Information
Diodes are classed as the simplest form of semiconductors but there is mainly three types of diodes that we have used in class; a normal diode, a Zener diode and also a LED (Light Emitting Diode). Diodes act as one way valves only allowing current to go in one direction, but Zener Diodes can not just be used as a regular diode in forward bias but in reverse it can regulate voltage, even though the Zener diode can be used two ways there is one thing it can't do that the LED can is light up in range of colours. The thing about diodes when all of them are in forward bias all have different Voltages drops with the normal diodes having the smallest Voltage drop of 0.6 Volts, then the Zener diode at 0.7 Volts and finally the LED at 1.8 Volts.Technical Explanation
A diode are a simple semiconductor device that has two terminal to be able to work as a one way valve in forward bias to only let current flow in one direction and place in reverse bias in circuit and block current from following into places you want to prevent current flowing to.Testing Procedures
The way to test a diode is pretty simple with a multimeter you set it to diode test mode, which is the mode on the multimeter with the diode symbol on it, the with the multimeter probes you place the ground on the Cathode side (grey band side) and the positive on the Anode (non grey band side), a good diode will give a voltage under 0.6V in forward bias but in reverse bias it will come up with either 0V or OL (Over Load). For the Zener diode it is the same but it will have a 0.7V reading for forward bias in diode test mode and will allow current to run through in reverse bias. The LED will be the same as the normal diode, OL for reverse bias and a 1.8V in forward bias for diode test mode.
Problems
The way to tell if a diode is faulty or not is that the diode should not be reading in both forward bias and reverse bias, or if the multimeter starts reading OL in both reverse bias and forward bias, both these ways will mean that the diode has shorted out. The technical term for the diode when it is reading in both directions is called a open shortage meaning if both sides of diode are emitting and if the diode is reading over loads or 0V on both side the diode will be classed as a shorted leaky diode,both of these storage's will make the diode unusable.
Reflection
The three diodes that I have used over the past few weeks have shown me that the diode is a good component to direct current, block current off, light up or regulate the voltage. being one the first semiconductors shows that this component has made a real impact within the Autoronic industry and have improved over time to make them more affective, using these components shows that they will be used in future more then they are now. While using all three diode I had to use the multimeter to find voltage drop and current, these components are very easy to test but easy to blow so I had to be really careful not to bridge the legs of the diodes together, it is a cheap component so it is easy to replace the diode if it has blown.Information Sources
- Hiller's Fundamentals of Automotive Electronics Book 2 Sixth Edition
- Resistor's Pages 23 - 25
- Diodes Pages 31 - 32
- Wikipedia
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Resistor
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diode
- Youtube
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cZFZc2r7aCM&feature=player_embedded (Resistor's)
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e2qCGpZ8wQ0&feature=player_embedded (Diode's)
- Google Images
- http://www.elexp.com
- http://www.amateur-radio-wiki.net/index.php?title=Resistors (Edited)
- http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Diode_pinout_en_fr.svg (Edited)
- http://reviseomatic.org/help/e-diodes/Diodes.php (Edited)
- http://www.lnwsiam.com/technology-article/electronic/5410-led-lcd- (Edited)